| Duration | 2.5 hours |
| Day | 2 of 2 |
Learning Objectives
By the end of this module, students will be able to:
- Create SWAIG functions using the @tool decorator
- Define parameters with proper types
- Handle function execution flow
- Return appropriate responses
Topics
1. What Are SWAIG Functions? (20 min)
Definition
SWAIG (SignalWire AI Gateway) functions extend your agent’s capabilities beyond conversation. They allow the AI to:
- Look up information
- Perform actions
- Integrate with external systems
- Make decisions based on data
How It Works
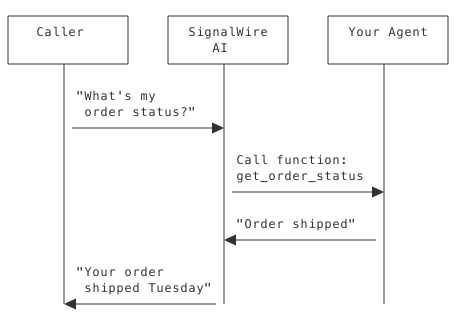
Function vs Conversation
| Conversation | Function |
|---|---|
| AI generates response | AI triggers your code |
| No external data needed | Can access databases/APIs |
| Immediate | May take time |
| Stateless | Can have side effects |
2. The @tool Decorator (30 min)
Basic Syntax
from signalwire_agents import AgentBase, SwaigFunctionResult
agent = AgentBase(name="my-agent")
@agent.tool(
description="Look up the current weather",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {"type": "string", "description": "City name"}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
)
def get_weather(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
city = args.get("city", "")
# Your logic here
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"The weather in {city} is sunny and 72°F.")
Decorator Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
description | str | Required. What the function does |
name | str | Override function name |
parameters | dict | Explicit JSON Schema |
secure | bool | Require authentication |
fillers | list | Phrases while executing |
Name Override
@agent.tool(
name="check_weather", # AI sees this name
description="Get current weather for a city",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {"type": "string", "description": "City name"}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
)
def get_weather_info(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
city = args.get("city", "")
# Function name in code can differ
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Weather in {city}: Sunny")
Security
@agent.tool(
description="Update account password",
secure=True, # Requires function token
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"new_password": {"type": "string", "description": "New password"}
},
"required": ["new_password"]
}
)
def update_password(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
new_password = args.get("new_password", "")
return SwaigFunctionResult("Password updated successfully.")
3. Parameters (35 min)
Type Hints (Automatic Schema)
The SDK generates JSON Schema from Python type hints:
@agent.tool(
description="Search products",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {"type": "string", "description": "Search query"},
"category": {"type": "string", "description": "Product category"},
"limit": {"type": "integer", "description": "Maximum results"}
},
"required": ["query"]
}
)
def search_products(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
query = args.get("query", "")
category = args.get("category") # Optional
limit = args.get("limit", 10) # Optional with default
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Found products matching '{query}'")
Generated Schema:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": { "type": "string" },
"category": { "type": "string" },
"limit": { "type": "integer" }
},
"required": ["query"]
}
Type Mapping
| Python Type | JSON Schema Type |
|---|---|
str | "string" |
int | "integer" |
float | "number" |
bool | "boolean" |
list | "array" |
dict | "object" |
Explicit Parameters
For more control, define the schema explicitly:
@agent.tool(
description="Record a rating",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"rating": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Rating from 1 to 5",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 5
},
"feedback": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Optional feedback text"
}
},
"required": ["rating"]
}
)
def record_rating(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
rating = args.get("rating", 0)
feedback = args.get("feedback", "")
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Thanks for the {rating}-star rating!")
Enum Parameters
Limit to specific values:
@agent.tool(
description="Transfer to department",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"department": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["sales", "support", "billing"],
"description": "Target department"
}
},
"required": ["department"]
}
)
def transfer_to_department(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
department = args.get("department", "")
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Transferring to {department}...")
4. Function Execution (25 min)
Return Values
Always return a SwaigFunctionResult:
from signalwire_agents import SwaigFunctionResult
@agent.tool(
description="Get account balance",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"account_id": {"type": "string", "description": "Account ID"}
},
"required": ["account_id"]
}
)
def get_balance(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
account_id = args.get("account_id", "")
# Fetch from database
balance = 1234.56
# Return result - AI will speak this
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Your account balance is ${balance}")
What Gets Spoken
The string in SwaigFunctionResult becomes part of the AI’s response:
return SwaigFunctionResult("Your order shipped on Tuesday.")
# AI might say: "I found your order. Your order shipped on Tuesday. Is there anything else?"
Raw Data Response
Return structured data for AI to interpret:
@agent.tool(
description="Get order details",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"order_id": {"type": "string", "description": "Order ID"}
},
"required": ["order_id"]
}
)
def get_order(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
order_id = args.get("order_id", "")
order = {
"id": order_id,
"status": "shipped",
"date": "2024-01-15",
"items": ["Widget A", "Widget B"]
}
return SwaigFunctionResult(str(order))
The AI will format this naturally in speech.
5. Fillers and Wait States (20 min)
Function Fillers
For functions that take time:
@agent.tool(
description="Search the database",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {"type": "string", "description": "Search query"}
},
"required": ["query"]
},
fillers=[
"Searching now...",
"Looking that up...",
"One moment while I search..."
]
)
def search_database(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
query = args.get("query", "")
# Slow operation
import time
time.sleep(2)
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Found 5 results for '{query}'")
Wait Files
Play audio while processing:
@agent.tool(
description="Process payment",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"amount": {"type": "number", "description": "Payment amount"}
},
"required": ["amount"]
},
wait_file="https://example.com/processing.mp3",
wait_file_loops=3
)
def process_payment(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
amount = args.get("amount", 0.0)
# Payment processing
return SwaigFunctionResult("Payment processed successfully.")
6. Testing Functions (20 min)
List Functions
swaig-test agent.py --list-tools
Output:
Available tools:
get_weather - Look up the current weather
Parameters:
city (string, required)
search_products - Search products
Parameters:
query (string, required)
category (string)
limit (integer)
Execute Functions
# Execute with arguments
swaig-test agent.py --exec get_weather --city "Seattle"
Output:
Executing function: get_weather
Arguments: {"city": "Seattle"}
Result: The weather in Seattle is sunny and 72°F.
Multiple Arguments
swaig-test agent.py --exec search_products --query "laptop" --limit 5
Complete Example
Click to reveal complete solution
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""Agent with SWAIG functions."""
from signalwire_agents import AgentBase, SwaigFunctionResult
agent = AgentBase(name="order-agent", route="/orders")
agent.prompt_add_section(
"Role",
"You help customers check their order status. "
"Ask for their order number to look it up."
)
agent.add_language("English", "en-US", "rime.spore")
# Simple function
@agent.tool(
description="Look up order status by order number",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"order_number": {"type": "string", "description": "Order number"}
},
"required": ["order_number"]
}
)
def get_order_status(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
order_number = args.get("order_number", "")
# In reality, query database
return SwaigFunctionResult(
f"Order {order_number} shipped yesterday via FedEx. "
f"Expected delivery is Thursday."
)
# Function with multiple parameters
@agent.tool(
description="Search for orders by customer email",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"email": {"type": "string", "description": "Customer email"},
"status": {"type": "string", "description": "Order status filter"}
},
"required": ["email"]
},
fillers=["Searching your orders...", "Looking that up now..."]
)
def search_orders(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
email = args.get("email", "")
status = args.get("status") # Optional
# In reality, query database
return SwaigFunctionResult(
f"Found 3 orders for {email}. "
"The most recent is order 12345, shipped Monday."
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
agent.run()
Common Mistakes
1. Missing Return Type
Wrong:
@agent.tool(description="Get info")
def get_info(id: str): # No return type hint
return "Info here" # Returns string, not SwaigFunctionResult
Right:
@agent.tool(
description="Get info",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {"type": "string", "description": "ID to lookup"}
},
"required": ["id"]
}
)
def get_info(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
id = args.get("id", "")
return SwaigFunctionResult("Info here")
2. Missing Description
Wrong:
@agent.tool() # No description!
def get_data(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
id = args.get("id", "")
return SwaigFunctionResult("Data")
Right:
@agent.tool(
description="Retrieve data by ID",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {"type": "string", "description": "ID to retrieve"}
},
"required": ["id"]
}
)
def get_data(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
id = args.get("id", "")
return SwaigFunctionResult("Data")
3. Poor Description
Wrong:
@agent.tool(description="Does stuff") # Too vague
Right:
@agent.tool(description="Look up customer account balance by account number")
The AI uses the description to decide when to call the function!
Key Takeaways
- @tool decorator - Easy function registration
- Type hints - Automatic parameter schema generation
- SwaigFunctionResult - Required return type
- Description matters - AI uses it to decide when to call
- Fillers help UX - Fill processing time naturally
- Test with swaig-test - Verify before live calls
Preparation for Lab 1.7
- Working agent with prompts and voice
- Understanding of function purpose
- Test data ready (fake order numbers, etc.)
Lab Preview
In Lab 1.7, you will:
- Add a lookup function to your agent
- Define parameters with proper types
- Test function execution with swaig-test
- Make a live call and use the function