| Duration | 2.5 hours |
| Day | 6 of 7 |
Learning Objectives
By the end of this module, students will be able to:
- Apply design patterns for voice AI systems
- Design scalable agent architectures
- Avoid common anti-patterns
- Document architectural decisions
Topics
1. Voice AI Design Patterns (40 min)
Pattern 1: Gateway Router
Central entry point distributes to specialized agents:
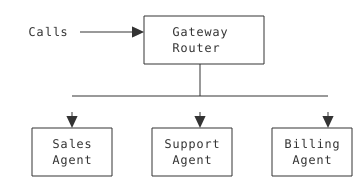
When to Use:
- Multiple specialized agents
- Need call routing logic
- Want centralized entry point
Implementation:
class GatewayAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="gateway", route="/")
@AgentBase.tool(
description="Route to department",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"department": {"type": "string", "description": "Department name"}
},
"required": ["department"]
}
)
def route(self, args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
department = args.get("department", "")
return (
SwaigFunctionResult(f"Connecting to {department}.")
.connect(f"/agents/{department}", final=True)
)
Pattern 2: Skill Composition
Build agents from reusable skill modules:
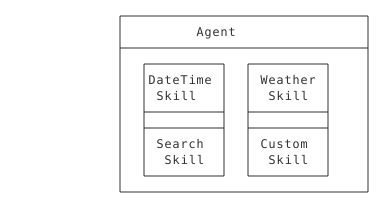
When to Use:
- Common functionality across agents
- Want maintainable, reusable code
- Team develops different capabilities
Implementation:
class SupportAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="support")
# Compose from skills
self.add_skill("datetime")
self.add_skill("web_search")
self.add_skill("custom_kb", kb_path="/data/support.json")
Pattern 3: Context State Machine
Structured workflows as state transitions:
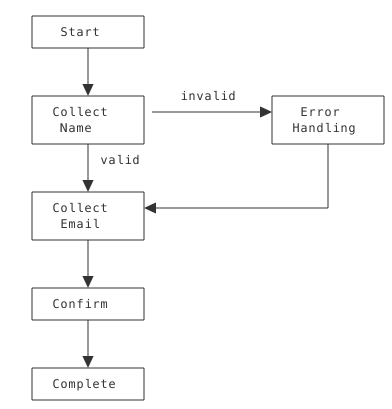
When to Use:
- Multi-step data collection
- Complex validation requirements
- Need to handle errors and retries
Pattern 4: DataMap Integration
Serverless external API integration:

When to Use:
- Simple REST API integration
- No custom logic needed
- Want to avoid webhook handlers
2. Scalability Patterns (30 min)
Horizontal Scaling
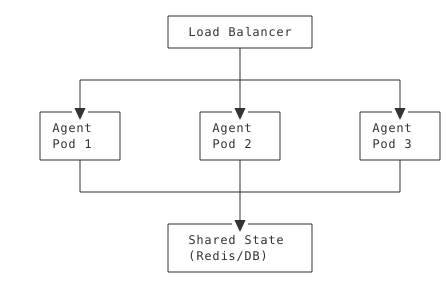
Key Considerations:
- Stateless agents (externalize state)
- Shared session storage
- Health checks for load balancer
- Auto-scaling policies
Stateless Agent Design
class StatelessAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self, redis_client):
super().__init__(name="stateless")
self.redis = redis_client
@AgentBase.tool(
description="Store customer data",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"call_id": {"type": "string", "description": "Call ID"},
"data": {"type": "object", "description": "Data to store"}
},
"required": ["call_id", "data"]
}
)
def store_data(self, args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
call_id = args.get("call_id", "")
data = args.get("data", {})
# Store in Redis, not local memory
self.redis.hset(f"call:{call_id}", mapping=data)
return SwaigFunctionResult("Data stored.")
@AgentBase.tool(
description="Retrieve customer data",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"call_id": {"type": "string", "description": "Call ID"}
},
"required": ["call_id"]
}
)
def get_data(self, args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
call_id = args.get("call_id", "")
data = self.redis.hgetall(f"call:{call_id}")
return SwaigFunctionResult(str(data))
3. Anti-Patterns to Avoid (25 min)
Anti-Pattern 1: Monolithic Agent
Problem: One agent does everything
# BAD: Giant agent with 50 functions
class EverythingAgent(AgentBase):
def sales_function_1(self): ...
def sales_function_2(self): ...
def support_function_1(self): ...
# ... 47 more functions
Solution: Split into focused agents
# GOOD: Specialized agents
class SalesAgent(AgentBase): ...
class SupportAgent(AgentBase): ...
class BillingAgent(AgentBase): ...
Anti-Pattern 2: Hardcoded Configuration
Problem: Configuration embedded in code
# BAD
agent.set_params({
"swml_basic_auth_password": "mysecret123" # In code!
})
Solution: Use environment variables
# GOOD
agent.set_params({
"swml_basic_auth_password": os.getenv("AUTH_PASSWORD")
})
Anti-Pattern 3: Synchronous External Calls
Problem: Blocking calls in functions
# BAD: Blocks for 30 seconds
@agent.tool(
description="Get data",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {"type": "string", "description": "Data ID"}
},
"required": ["id"]
}
)
def get_data(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
id = args.get("id", "")
response = requests.get(f"https://slow-api.com/{id}") # 30s timeout
return SwaigFunctionResult(response.json())
Solution: Use timeouts and async patterns
# GOOD: With timeout and error handling
@agent.tool(
description="Get data",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {"type": "string", "description": "Data ID"}
},
"required": ["id"]
},
fillers=["Looking that up...", "Still searching..."]
)
def get_data(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
id = args.get("id", "")
try:
response = requests.get(
f"https://api.com/{id}",
timeout=5 # 5 second max
)
return SwaigFunctionResult(response.json())
except requests.Timeout:
return SwaigFunctionResult(
"I'm having trouble reaching that system. "
"Can I help with something else?"
)
Anti-Pattern 4: Exposing Internal Errors
Problem: Technical errors exposed to callers
# BAD
except Exception as e:
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Error: {str(e)}")
# Caller hears: "Error: ConnectionRefusedError: [Errno 111]..."
Solution: User-friendly error messages
# GOOD
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Function failed: {e}")
return SwaigFunctionResult(
"I'm having trouble with that right now. "
"Would you like me to transfer you to someone who can help?"
)
4. Documentation Practices (25 min)
Architecture Decision Records (ADRs)
Document why, not just what:
# ADR 001: Multi-Agent vs Single Agent
## Status
Accepted
## Context
We need to support sales, support, and billing functions.
## Decision
Use separate agents for each department with a gateway router.
## Consequences
- Pros: Easier to maintain, team can work independently
- Cons: More complex deployment, need shared state solution
Agent Documentation Template
# Sales Agent
## Purpose
Handle sales inquiries and pricing questions.
## Endpoints
- SWML: `/sales`
- SWAIG: `/sales/swaig`
## Functions
| Function | Description | Parameters |
|----------|-------------|------------|
| get_pricing | Get product pricing | product (string) |
| check_availability | Check product stock | sku (string) |
## Dependencies
- Product database
- Pricing API
## Configuration
| Variable | Description | Default |
|----------|-------------|---------|
| PRODUCT_API_URL | Product API endpoint | - |
| CACHE_TTL | Cache duration | 300 |
Key Takeaways
- Patterns provide structure - Use proven approaches
- Scale horizontally - Design for multiple instances
- Avoid anti-patterns - Learn from common mistakes
- Document decisions - Future you will thank you
- Keep agents focused - Single responsibility principle
Preparation for Lab 3.1
- Review your Level 2 projects
- Identify architectural patterns used
- List potential improvements
Lab Preview
In Lab 3.1, you will:
- Design a multi-agent architecture
- Document with ADRs
- Identify and fix anti-patterns
- Present architecture review