| Duration | 2 hours |
| Day | 6 of 7 |
Learning Objectives
By the end of this module, students will be able to:
- Optimize agent response times
- Configure speech and timing parameters
- Reduce latency in function calls
- Profile and benchmark agent performance
Topics
1. Voice AI Performance Factors (20 min)
The Latency Stack
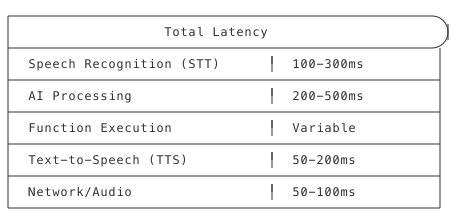
Performance Goals
| Metric | Good | Acceptable | Poor |
|---|---|---|---|
| First response | <1s | 1-2s | >2s |
| Function response | <500ms | 500ms-1s | >1s |
| Total turn latency | <2s | 2-3s | >3s |
2. Speech Timing Configuration (30 min)
Attention Timeout
How long to wait for user to start speaking:
agent.set_params({
"attention_timeout": 10000, # 10 seconds
"attention_timeout_prompt": "Are you still there?"
})
End of Speech Detection
Balance between responsiveness and interruption:
agent.set_params({
# Time to wait after user stops speaking
"end_of_speech_timeout": 500, # 500ms default
# Barge-in settings (barge is enabled by default)
"barge_min_words": 2 # Require 2 words to interrupt
})
Speed Control
agent.set_params({
"speech_rate": 1.0, # 1.0 = normal, 1.2 = faster
"ai_volume": 1.0 # Volume level
})
Timing Comparison
| Setting | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Short timeout (300ms) | Quick transactions, confirmations |
| Medium timeout (500ms) | Normal conversation |
| Long timeout (800ms) | Thoughtful answers, elderly callers |
3. Function Performance (35 min)
Fillers for Long Operations
Keep the caller engaged during processing:
@agent.tool(
description="Search inventory",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {"type": "string", "description": "Search query"}
},
"required": ["query"]
},
fillers=[
"Let me check on that...",
"One moment while I search...",
"Still looking..."
]
)
def search_inventory(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
query = args.get("query", "")
# Long operation
results = database.search(query)
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Found {len(results)} items.")
Timeout Handling
import requests
from requests.exceptions import Timeout
@agent.tool(
description="Get order status",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"order_id": {"type": "string", "description": "Order ID"}
},
"required": ["order_id"]
}
)
def get_order(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
order_id = args.get("order_id", "")
try:
response = requests.get(
f"https://api.example.com/orders/{order_id}",
timeout=3 # 3 second max
)
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Order status: {response.json()['status']}")
except Timeout:
return SwaigFunctionResult(
"I'm having trouble reaching our order system. "
"Can I take your number and call you back?"
)
Async Patterns
import asyncio
import aiohttp
class AsyncAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="async-agent")
self._setup_functions()
def _setup_functions(self):
@self.tool(
description="Check multiple systems",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {},
"required": []
},
fillers=["Checking all systems..."]
)
async def check_all_systems(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
# Parallel requests
tasks = [
self.check_system(session, "inventory"),
self.check_system(session, "shipping"),
self.check_system(session, "billing")
]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True)
# Summarize results
statuses = [r for r in results if not isinstance(r, Exception)]
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Systems checked: {len(statuses)} operational")
async def check_system(self, session, system):
async with session.get(f"https://api.example.com/{system}/health") as resp:
return await resp.json()
Caching Strategies
from functools import lru_cache
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
class CachedAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="cached-agent")
self._cache = {}
self._cache_ttl = timedelta(minutes=5)
def _get_cached(self, key: str):
if key in self._cache:
value, timestamp = self._cache[key]
if datetime.now() - timestamp < self._cache_ttl:
return value
return None
def _set_cached(self, key: str, value):
self._cache[key] = (value, datetime.now())
@AgentBase.tool(
description="Get product pricing",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"product_id": {"type": "string", "description": "Product ID"}
},
"required": ["product_id"]
}
)
def get_pricing(self, args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
product_id = args.get("product_id", "")
# Check cache first
cached = self._get_cached(f"price:{product_id}")
if cached:
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Price: ${cached}")
# Fetch and cache
price = self.fetch_price(product_id)
self._set_cached(f"price:{product_id}", price)
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Price: ${price}")
4. Prompt Optimization (25 min)
Concise Prompts
# BAD: Too verbose
self.prompt_add_section(
"Role",
"You are a highly skilled and knowledgeable customer service "
"representative working for our esteemed company. Your primary "
"responsibility is to assist customers with their inquiries in "
"a professional, courteous, and efficient manner while maintaining "
"the highest standards of service excellence..."
)
# GOOD: Clear and concise
self.prompt_add_section(
"Role",
"Customer service agent for TechCorp. Help with orders, "
"returns, and product questions."
)
Structured Instructions
# Use bullets for clarity
self.prompt_add_section(
"Response Guidelines",
bullets=[
"Keep answers under 2 sentences when possible",
"Confirm understanding before taking action",
"Offer alternatives if request can't be fulfilled"
]
)
Focused Context
# Only include relevant information
class FocusedAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self, department: str):
super().__init__(name=f"{department}-agent")
# Department-specific prompt only
if department == "sales":
self._setup_sales_prompt()
elif department == "support":
self._setup_support_prompt()
def _setup_sales_prompt(self):
self.prompt_add_section(
"Role",
"Sales agent. Help with pricing and purchases."
)
# Only sales-relevant info
def _setup_support_prompt(self):
self.prompt_add_section(
"Role",
"Support agent. Troubleshoot issues."
)
# Only support-relevant info
5. Profiling and Benchmarking (30 min)
Measuring Performance
import time
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class ProfiledAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="profiled-agent")
self._setup_functions()
def _setup_functions(self):
@self.tool(
description="Profiled function",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {"type": "string", "description": "Query to process"}
},
"required": ["query"]
}
)
def my_function(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
query = args.get("query", "")
start = time.perf_counter()
# Your logic here
result = process_query(query)
elapsed = time.perf_counter() - start
logger.info(f"my_function took {elapsed:.3f}s")
return SwaigFunctionResult(result)
Performance Decorator
import functools
import time
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def profile(func):
"""Decorator to profile function execution time."""
@functools.wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.perf_counter()
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
elapsed = time.perf_counter() - start
logger.info(f"{func.__name__}: {elapsed:.3f}s")
return result
return wrapper
class OptimizedAgent(AgentBase):
@profile
def _process_order(self, order_id: str):
# Implementation
pass
Load Testing
# Using hey for HTTP load testing
hey -n 100 -c 10 \
-m POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{}' \
http://localhost:3000/agent
# Using locust for complex scenarios
# locustfile.py
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
class AgentUser(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 3)
@task
def call_agent(self):
self.client.post("/agent", json={})
@task
def call_function(self):
self.client.post("/agent/swaig", json={
"function": "get_status",
"args": {}
})
Performance Dashboard
from datetime import datetime
from collections import defaultdict
class MetricsAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="metrics-agent")
self.metrics = defaultdict(list)
def record_metric(self, name: str, value: float):
self.metrics[name].append({
"value": value,
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat()
})
def get_metrics_summary(self):
summary = {}
for name, values in self.metrics.items():
vals = [v["value"] for v in values]
summary[name] = {
"count": len(vals),
"avg": sum(vals) / len(vals) if vals else 0,
"min": min(vals) if vals else 0,
"max": max(vals) if vals else 0
}
return summary
Performance Optimization Checklist
Speech Settings
- Appropriate attention timeout
- End-of-speech timeout tuned
- Barge-in configured if needed
Function Performance
- Timeouts on all external calls
- Fillers for slow operations
- Caching where appropriate
- Async for parallel operations
Prompts
- Concise system prompt
- Only necessary context included
- Clear, structured instructions
Monitoring
- Performance logging enabled
- Key metrics tracked
- Alerts for degradation
Key Takeaways
- Latency is cumulative - Every millisecond counts
- Use fillers - Keep users engaged during processing
- Timeout everything - Never block indefinitely
- Cache wisely - Fresh data vs. speed tradeoff
- Measure constantly - Can’t improve what you don’t measure
Preparation for Lab 3.3
- Identify slow functions in your agents
- Gather baseline performance metrics
- List external dependencies
Lab Preview
In Lab 3.3, you will:
- Profile an existing agent
- Implement caching and timeouts
- Configure optimal speech settings
- Measure improvement with load testing